Physiotherapists
Since each disease has a different prognosis and pathology, the physiotherapist chooses and applies the most appropriate agent for treatment using his knowledge and skills. These agents have many physiological effects, from increasing blood flow in tissues to post-synaptic inhibition and blockade of pain.
Superficial and deep temperature agents: Hot-pack, paraffin, infrared, fluidotherapy, short wave diathermy, long wave diathermy, microwave diathermy, ultrasound.
Cold agents: Cold-pack, cryotherapy.
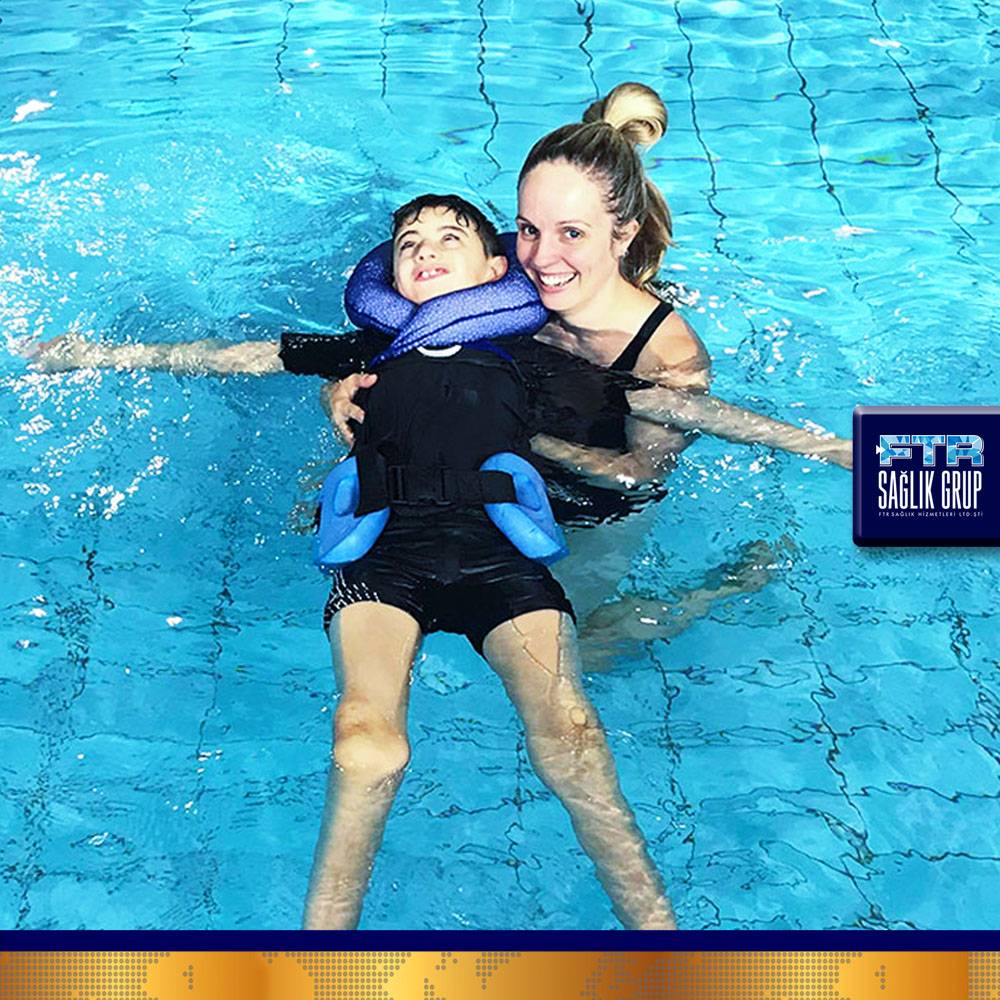
Hydrotherapy methods: Immersion baths, opposite baths, whirlpool baths (whirlpool), butterfly bath (hubbard tank), opposite showers, hydromassage, underwater traction bath, galvanic bath, balneotherapy.
Electrotherapy agents: Galvanic current, faradic current, diadynamic currents, TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation), interference currents, BEMER (bio electromagnetic energy regulation).
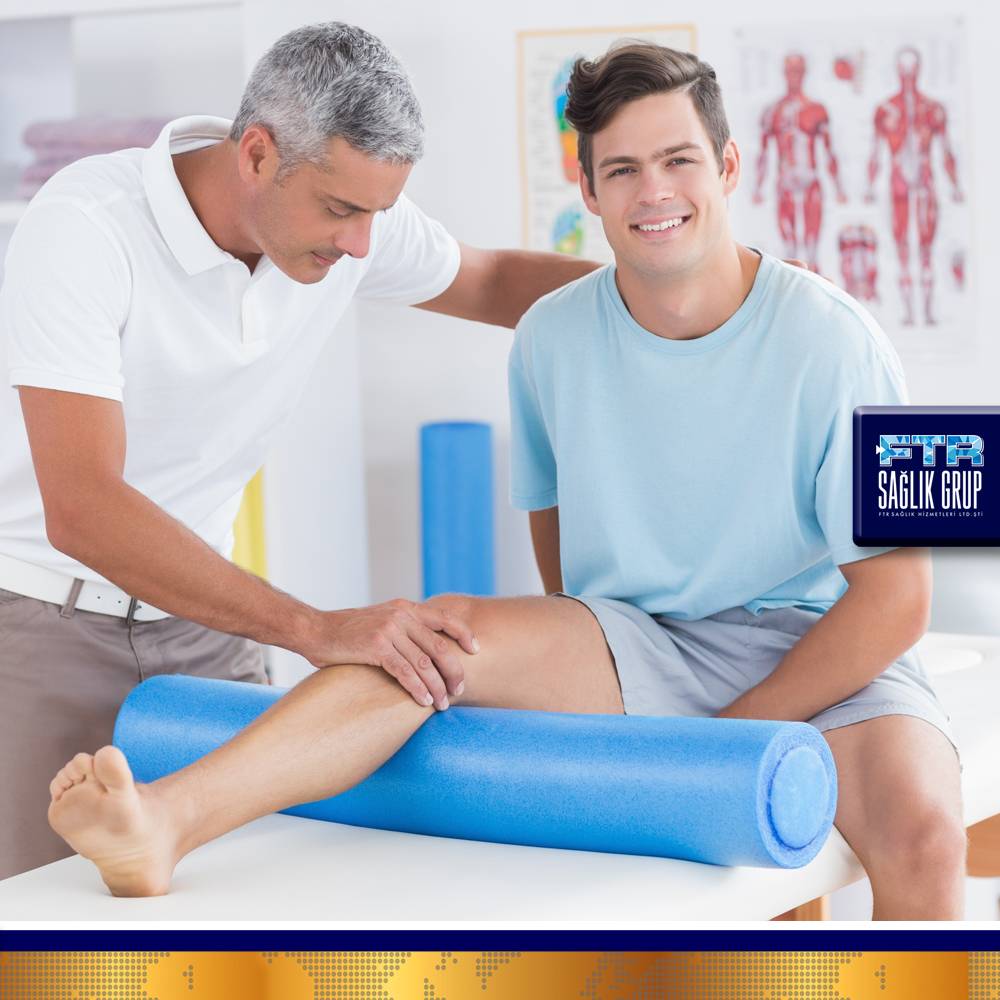
Manipulative treatment methods: Classical massage, connective tissue massage, lymphedema drainage, mobilization and manipulation techniques.
Custom Fields
Physiotheraphy
muscle diseases
cardiopulmonary rehabilitation
athlete health
neurosurgery
Obstetric-urogynecological physiotherapy
Orthotics-prosthesis and biomechanics
rheumatic diseases
Geriatrics
neurology
orthopedics
Pediatrics
Dermatology
oncology